What is Administrative Law
A core principle of democracy is that citizens are entitled to be treated equally under the law, but they must also submit to the rule of law and regulations designed to protect the public interest. Administrative law offers the legal framework enabling the government to create regulations that align with the collective interests of society. Administrative law also specifies how individuals may seek to challenge rules; assert particular rights; or obtain appropriate remedies from agencies in case of improper agency action. Understanding the scope of administrative law is essential for a modern legal practitioner, as well as for any other professional engaged with industries subject to significant federal and state regulation.
Administrative law is a complex and far-reaching area of the law , establishing the procedures under which federal and state governmental agencies operate. Administrative law dictates, among other things, how laws are created and made by agencies, how powers are delegated from one entity to another, and sets rules for judicial review and enforcement. Often, administrative law and administrative decisions in general have the effect of law, especially in specialized areas of law like tax, environmental protection, safety, and human rights. Administrative decision-making is only reviewed by the judiciary in exceptional circumstances, making administrative law an integral part of the modern legal landscape.
Administrative Law Flowchart
An admin law flowchart is a visual representation of the rules and procedures governing adjudications and investigations in the realm of administrative law. Admin law flowcharts help provide clarity for a complicated "flow" of rules. They help the reader visualize a process and the implications once triggered. But an admin law flowchart does not reveal the legal minutiae and it is not a strict interpretation of regulations or statutes. Administrative law will require a reader to search for a relevant regulation or statute and to have a command over those legal materials in order to make a final determination. In that way, an admin law flowchart merely provides a simplified overview of government procedures.
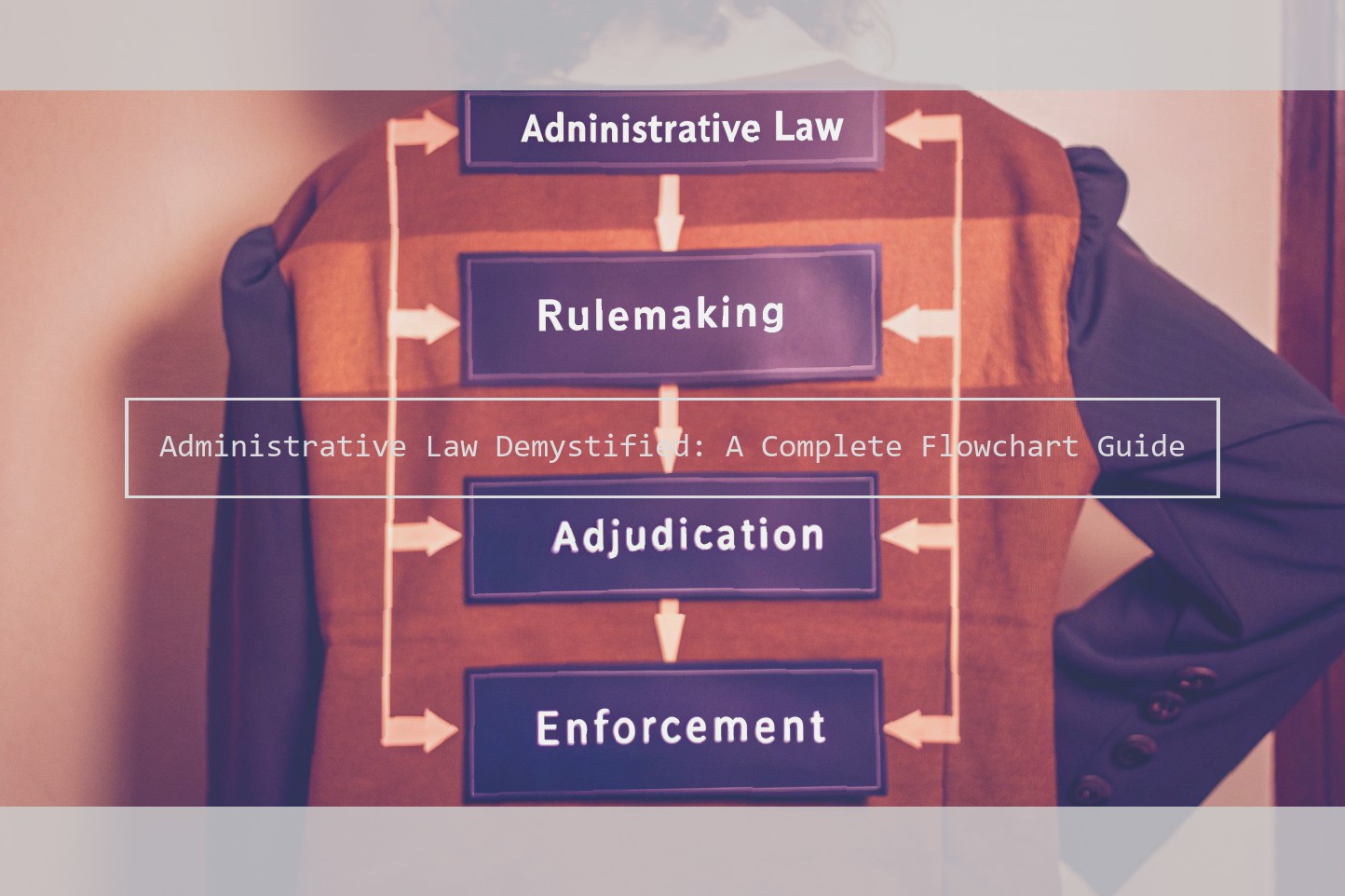
The Core Elements of Administrative Law
At the federal level, administrative law is a very important and major part of our legal system. Administrative law is made up of rules and regulations that are created by the various administrative agencies. Essentially, administrative agencies are given power by Congress to exercise both legislative and administrative (executive) responsibilities to carry out the laws set by Congress.
Administrative law can be broken down into three main components:
Rulemaking
Adjudication
Enforcement
Rulemaking is exactly what it sounds like – the creation of laws in the form of rules and regulations. In this role, administrative agencies can create rules and regulations on behalf of Congress that assist with compliance issues. Although written by an agency, rules and regulations drafted and enacted are treated as law.
Adjudication is the role of agencies as an adjudicator or judge. They make judgments on cases filed before them. For example, the Social Security Administration conducts a hearing for someone who applies for disability benefits and is denied. If action is not taken administratively, the person may then file a civil action in federal court to further litigate the issue.
Enforcement is the act of executing and enforcing the law. Federal agencies are responsible for enforcing the rules and laws under their jurisdiction. For example, legally speaking, a bankruptcy discharge orders creditors to cease all harassment and stop operation of collection efforts. As such, enforcement would be the filing of motions in bankruptcy court to hold a creditor in contempt for violating the discharge order and for additional damages such as attorney fees and expenses.
These three components form the backbone of administrative law and outline the most common functions performed.
Admin Law Flow Chart – How to Create an Effective Chart
When embarking on a journey of creating an effective administrative law flowchart, you should begin by gathering all of the necessary information. You’ll need to identify all relevant processes and decisions in order to begin laying out your flowchart.
First, identify the primary process or decision that requires clarification. It could be a complex regulatory decision, or simply a matter of fact and law that needs to be clarified before a hearing can take place. The next step in this phase involves the identification of all relevant agency processes, decisions and related facts that will affect your case. It is important to limit the scope of your inquiry to those specific processes and facts as this will help streamline which decisions you will need to address in the flowchart. You will also need to identify on what basis those specific processes and facts were decided and detail how they might affect the outcome of your case.
The second phase to creating a comprehensive administrative law flowchart involves mapping and eliminating any redundant or ineffective processes. Oftentimes a straightforward competitive system can become confusing under administrative review. It is important to find redundancies to ensure you are only drawing attention to those critical sections of law or related facts that directly affect the outcome of your case. One way you can do this is by identifying and cataloguing relevant sections of law or facts that have changed since the primary decision was made. Additionally, you can look for small process flaws that can negatively affect how you view the overall process.
The final phase of creating an effective administrative law contract entails using flowchart and presentation software to guide your creations. Software programs such as Microsoft Visio and Smartdraw allow you to drag and drop boxes, and build your flowchart in a quick and effective manner. Moreover these software programs allow you to identify redundancies and reorganize boxes based on your needs.
The Advantages of Using Flowcharts in Administrative Law Proceedings
There are several benefits to using flowcharts in the context of administrative law proceedings. First and foremost, flowcharts bring a new level of understanding to the often detailed, convoluted and complex processes that occur during these types of administrative law proceedings. These proceedings include applications before administrative agencies, the drafting of hearings and appeals, and investigations and discovery. By following the flowchart, the reader will understand quickly and easily complex procedural steps, standard timelines and relevant authorities.
In addition, flow charts promote efficient and effective communication among stakeholders. For example, a clear depiction or representation of these various steps or processes vis-a-vis a flow chart can be useful in promoting a much larger discussion of important issues – particularly as they relate to agency regulation at large, as opposed to the specific agency action being undertaken. By way of comparison, if you were involved in an application matter at an administrative agency, you would want your application to be considered in the context of similar application events before the same agency and/or similar or related events before other agencies. A flow chart can be very useful in terms of starting that dialogue and/or communicating that agency-wide position to necessary stakeholders.
In the same vein, a flow chart can be particularly useful for demonstrating your organization’s process for a specific type of hearing or appeal – many organizations have developed an administrative hearing or appeal guidebook, but a flowchart can be a new, helpful tool in terms of these types of entrepreneurial efforts. This is not to say that one tool is any more useful than another, but that both have their uses and should be utilized together and iteratively, in the appropriate context and communication/networking channels for each administrative proceeding.
Finally, flow charts can be a useful way to streamline administrative decisionmaking. This is particularly true with agencies that have relatively short and stringent decisions deadlines to meet. A flow chart with clearly defined decisionmaking steps and timelines can keep everyone on track to meet those stringent deadlines. In addition, by capturing and visualizing those decisionmaking parameters in a graphical format, administrative decisionmakers can now expand their understanding and analyze those decisionmaking processes for further efficiencies down the road.
Case Examples: Administrative Law Flow Charts Effectively Utilized for Cases
"Case law is the story of those who have gone before us in the realm of administrative procedure." Every expert on administrative law tells us to read the cases, but most administrative law practitioners have a hard time getting through them. Reviewing these cases through various flowcharts shows how flowcharting a process makes that process easier to read and understand. Example 1: A local unit of government enters into a contract with an employee for the sale of new furniture, even though the contract was never authorized by the Board of Aldermen. The local unit of government subsequently refuses to pay the contract price . A flowchart of this situation provides a better understanding of whether the local unit of government is liable to the employee: Example 2: An employee of a township petitions for tenure flowchart of this situation shows how tenure is lost. The tenure petition is submitted to the Superintendent of Schools who fails to submit the petition to the Board of Education. Example 3: An employee of a municipality petitions an arbitrator to compel the municipality to provide a grievance arbitration. An analysis of the facts of the grievance and then application of the governing collective bargaining agreement shows that the grievance is not arbitrable.
Avoiding Mistakes When Creating Administrative Law Flow Charts
Creating a flowchart appears simple enough: It is a series of labeled arrows and boxes. But poor design falls into the same traps as dense text. Inaccurate, exclusionary, or misleading arrows stitch together a narrative that will leave your users confused. Though focused on a very specific process, Schaffer Flowchart: Firing Up a New Location is also appropriately Spaghetti, since the arrows conflict with the text. After the "Launch Party?", the next arrow points to "Before Opening", which is not sequential to the final step "Open". The arrows should connect to a proper section (such as "Pre-opening Steps") to prevent confusion. The arrows on the Schaffer Flowchart can only make sense if a user reads the legend carefully. "Notify PMC" is not followed by which PMC, so one can only assume it refers to two separate people working at the same time. However, it is easier to assume that the arrows are simply pointing to the wrong section. When designing a flowchart, the order of the steps is important; misdirected arrows will confuse readers. Some designers may think that using an arrow to connect two unrelated sections is acceptable, since it can represent an explosion to another part of the company. But to the user, the arrow can cause more confusion than understanding. An event that causes another event is not automatic, and requires additional steps to connect. Four sequential steps make up the flowchart to Explain Payroll, an example used in Good Communication: Using Flow Charts for Employee Procedures, a blog post I wrote about ChartSolutions. The arrows are sequential and easy to follow. Once you’ve established a shorthand for your flowchart, the best practice is to use that shorthand throughout. Take the Jaclyn "Jackie" Kennedy Onassis and the JFK Assassination timeline from Timelines.com. Here, JFK is shown as subject to multiple deaths. Yes, Timothy McCarthy is also known for assassination attempts; however, the death of both John and Jackie are not actually related in history. It is acceptable to use an abbreviation (here-inafter abbreviated as [babe]) for Jacqueline Kennedy Onassis, but only if it’s consistent (when she’s alive). When using an abbreviation, define what it means at least once for the reader. An abbreviation should carry over with the reader from one page to the next. With timelines, as with flowcharts, you have to decide what is important to include, and what can be edited out, leaving only the useful information. Timelines immediately preceding or following an event should be included, but extraneous information on the timeline is not necessary. Error messages, like the one shown in this screenshot from Slack, provide an example of an untenable flowchart. The arrow directed users to refresh, but the screenshot of a message from a Slack administrator told them to issue a request for help. The decision on whether to refresh is confusing as a result. (Presumably the instruction to malware daring the user to click it is a mistake, and should be an actual warning.) This flowchart from Timelines.com shows how confusing a diagram can be if it doesn’t provide a reference to prior knowledge. The system they show for voting and determining the next move is overly complex, partly because it’s designed to be comprehensive. When is an open primary better than a closed primary? That is for a political scientist to determine. The example serves mostly to show the importance of knowing your audience. Focus on what your users need, not what’s interesting. Describing the process of flossing your teeth, this chart from Visualistan is less informative than it is confusing. The arrows have overlapping paths, and the black arrows lead to the wrong section of the chart. "Yank" also doesn’t mean what they mean. In general, avoid using unusual words and terms in your flowchart.
The Future of Administrative Law Visibility and Interactive Flowcharts
As we look toward the future, the potential for administrative law visualization continues to grow along with technological advancements. In recent years, there has been an increasing trend toward using technology, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning, to streamline legal processes. The future of administrative law visualization may see even greater integration with these technologies, making flowcharts not only a static representation of a process but also an interactive, intelligent guide that can provide real-time support and guidance.
One emerging area is the use of virtual assistants or "chatbots" that can provide users with instant access to legal information and advice. These virtual assistants could be capable of analyzing user data and providing customized legal advice based on individual needs. Such tools could be integrated into flowcharts to enhance the user experience and provide a more seamless interface between the user and the law.
Another area of growth is the use of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) to visualize complex legal processes. With AR and VR, users can explore different scenarios and outcomes in a more immersive way, allowing them to better understand administrative law processes and make more informed decisions. These technologies could be used to create dynamic flowcharts that respond to user input and provide a more interactive experience.
As these technological trends continue to evolve, it will be important to keep in mind the ethical implications of using such tools. Ensuring that these tools are user-friendly, reliable and secure will be paramount to their adoption by the legal community. However, the potential for administrative law visualization to both enhance and streamline legal processes is significant, and can have a lasting impact on how we interact with the law now and in the future.
Conclusion: Flowcharts as a Vital Tool in Administrative Law
Grasping administrative law can be challenging; however, with the help of a well-designed flowchart, administrators can make the concept easier to understand and implement effectively. The above information provides a comprehensive, illustrative overview of the steps in an administrative law process. As noted , proceeding beyond this general guide is possible only through the review of the specific text of the administrative law in question. Flowcharts can also have other helpful applications in terms of administrative law. For example, they can help to identify possible loopholes and complexities. Additionally, they can clarify steps needed to resolve an apparent administrative law breakdown. They can also help with the implementation of updates in the regulatory structure that may be difficult to absorb in other contexts.

+ There are no comments
Add yours